What is in Your IV Bag Understanding Intravenous (IV) Fluids for Health
What is the most important, yet often overlooked, part of your IV therapy drip? The answer isn't the vitamin blend—it’s the base liquid that delivers those ingredients. When you choose IV therapy for rapid energy, immune support, or recovery, these intravenous fluids are carefully selected to ensure maximum absorption without shocking your system. They are the essential foundation of any successful hydration or nutrient infusion.
Intravenous fluids (IV fluids) are much more than simple water. They represent the core of intravenous therapy, serving as highly controlled electrolyte solutions essential for maintaining life and maximizing wellness. Understanding the precise composition and effects of the fluid you receive is paramount to effective fluid management and improving your overall fluid status. Every Primary IV Fluid Infusion begins with this fundamental choice.
Crystalloid Solutions The Core of IV Therapy
Crystalloid solutions are the most common intravenous fluids used in both Critical Care and wellness IV therapy. They contain small molecules that pass easily between the blood vessels and the surrounding tissues, making them the most efficient method for correcting a fluid deficit and addressing generalized fluid losses.
A. Normal Saline
Normal saline (0.9% sodium chloride), also known as normal saline solution, is an isotonic solution. It is the gold standard for immediate fluid resuscitation.
- Therapeutic Uses It is primarily used to expand the extracellular fluid volume and is essential for managing vascular volume loss. Crucially, it is the only IV fluid compatible with blood products and for initiating blood transfusions with packed red blood cells.
- Caution High volumes of fluid administration can lead to hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis, characterized by a potential elevation in the anion gap. This risk is a key factor in long-term fluid therapy.
B. Lactated Ringer's Solution (LR)
Lactated Ringer's solution is the preferred balanced IV fluid. Also isotonic, it is often called Ringer's Lactate or Ringer's solution. It contains sodium chloride along with lactate, which the liver converts to sodium bicarbonate.
- Therapeutic Uses LR is superior for large-volume fluid resuscitation and restoring the balance of fluid and electrolytes. The bicarbonate conversion helps manage certain forms of metabolic acidosis without the risk of worsening hyperchloremia, though it is contraindicated in patients with severe lactic acidosis. It is commonly used for managing conditions like Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA).
- Serum Electrolytes LR is formulated to closely mimic the body's serum electrolytes and plasma concentration.
C. Dextrose 5% in Water (D5W)
Dextrose 5% in Water starts as an isotonic solution, but once the body metabolizes the dextrose (sugar), the remaining free water turns the solution functionally hypotonic. It is often used as a diluent for IV medications or as a secondary IV fluid delivered via IV piggyback.
Tonicity The Movement of Fluid
Tonicity describes the concentration of solutes in the intravenous solutions relative to the cell, dictating how dramatic the fluid shifts will be.
A. Isotonic Fluids
As mentioned (normal saline and LR), these are balanced and are ideal for increasing blood volume and stabilizing Blood pressure. They are the safest choice for hydration drips and vitamin drips.
B. Hypotonic Fluids
Hypotonic fluids have a lower solute concentration than the blood. They cause water to move from the blood vessels into the cells.
- Therapeutic Uses Used when cellular rehydration is needed (e.g., treating high serum sodium).
- Caution Rapid fluid administration can cause cerebral fluid overload and is a major risk factor for cerebral edema.
C. Hypertonic Solutions
Hypertonic solutions have a higher solute concentration than the blood. They pull water out of the cells and into the blood vessels.
- Therapeutic Uses Highly concentrated solutions are sometimes used in Critical Care to reduce severe swelling and fluid accumulation, especially in cases of impending cerebral edema.
- Caution These solutions must be administered slowly and carefully to avoid cellular dehydration and dangerous fluid overload.
Colloid Solutions (Non-Crystalloids)
A colloid solution contains large molecules that are too big to easily leave the blood vessels.
- Primary Purpose They are mainly used to rapidly expand the circulating blood volume and treat vascular volume loss as they stay in the plasma space for longer. They are less common in wellness intravenous therapy than crystalloids.
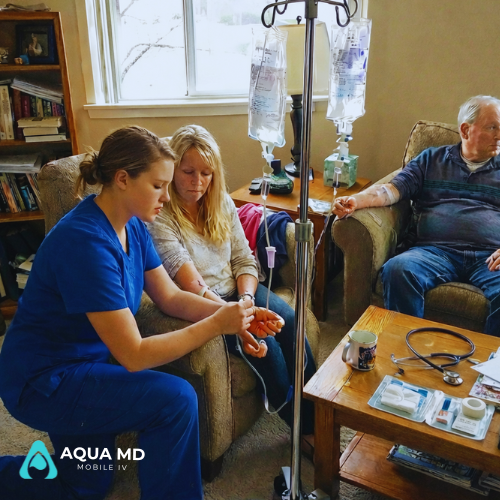
Aqua MD IV Therapy Customizing Your Fluid Therapy
At Aqua MD, our approach to fluid therapy prioritizes safety and effectiveness. We utilize isotonic crystalloid solutionsas the stable base for all our drips, ensuring proper fluid balance and minimal risk while allowing rapid delivery of IV medications and nutrients.
- Aqua Detox IV therapy provides comprehensive fluid and electrolytes replacement, aiding in systemic detoxification that assists with cellular waste excretion.
- Aqua Immunity and Aqua Beauty use the isotonic carrier to facilitate the maximum bioavailability of high-dose vitamins and antioxidants.
- The Aqua Performance drip specifically targets athletes by combining the base IV fluid with NAD+ and complexes designed to replace fluid deficit and support muscle repair.
- For rapid response, Aqua Restore STAT uses the base IV fluid for rapid delivery of symptom-relieving IV medications.
Proper fluid status is the prerequisite for all health optimization. Our specialized packages—including Aqua Slim, Aqua Reset IV, and Aqua Balance—all start with this rigorous scientific approach to fluid management, delivered comfortably to you.
Book your consultation today to discuss the therapeutic uses of our customized IV fluids and IV therapy options.